When you think of welding, normally fusion and heating come to your mind; however, in cold welding, as the name suggests, the welding or joining of two metal parts happens at ambient temperature and under pressure. Cold welding of ductile metals such as aluminum, copper, lead, etc., are very popular.
Cold welding is used for joining wires as well as to join metals together in space, this process had a range of applications across industry. Other industries that often use cold welding include the automotive industry and advanced fabrication applications.
This article will discuss cold welding in space, cold welding aluminum and other metals, cold welding with TIG, pros and cons of cold welding, and related topics.
What is Cold Welding, and How it Happens?
Most of us know how welding occurs in any workshop. We heat the two metal parts to be welded to their melting temperature and allow them to fuse together.
Different types of welding, like arc welding, TIG welding, laser welding, etc., cannot be done without using heat energy. Heat is used in the welding process to make the two metals soft enough to diffuse with each other or with a third metal (filler).
Cold welding is not done with heat. Also referred to as contact welding, it is a solid-state welding process between the two pieces of metal under pressure or, in other words, the atoms of the two metals are joined and diffused together. The surface of the two metal parts being cold-welded should be flat and thoroughly cleaned. The amount of pressure required for welding differs from metal to metal.
In our daily life, we might have brought two flat pieces of the same metal (say aluminum) into contact or rubbed it, and nothing happened. However, if you thoroughly clean both the metal parts’ surfaces and bring them together into contact under vacuum, the two metal aluminum parts will stick with each other. This phenomenon is called cold welding or cold pressure welding.
When exposed to atmospheric oxygen, the two flat parts of the same metal (say aluminum) form an oxide layer on the metal surface. This layer of oxide, along with other impurities like grease or oil on the surface act as a barrier preventing the metal atoms from bonding. And welding does not happen even if you bring the two flat pieces into contact with one another and apply pressure on them.
However, you can thoroughly clean the surface layers (to remove the oxide layer and other impurities) and bring the two parts into contact under vacuum (no oxygen). The oxide layer and other impurities can be removed by degreasing, wire brushing, or mechanical and chemical methods. This is essential because the wire brush can force these impurities deeper into the metal.
Then, the two pieces get cold-welded because the atoms contained in both the aluminum parts cannot differentiate and jump into each other creating a physical bond. This bond’s strength will become as good as the parent metal because the workpieces are pressed together to make the surface contact 100 percent (when you apply pressure, the vacuum is not required). The correct pressure applied to both the metal parts help to make the surface contact 100 percent.
Watch the following video explains the joining of two parts under vacuum.
The facts about cold welding were recognized as early as 1940. It was learned that when two similar metals (with thoroughly cleaned flat surfaces) are brought into mutual contact under a vacuum, they adhere together to create a strong bond.
Types of Metal for Cold Welding
The main prerequisite for cold welding method is that the metals to be cold-welded are ductile. And the surface should be flat and clean and be of a regular shape. The strongest cold welds are achieved with flat, regular surfaces. Cold welding can create strong joints between wires.
Non-ferrous metals like aluminum, copper, 70/30 brass, lead, gold, nickel, silver, silver alloys, and zinc, are suitable for cold welding.
Is Cold Welding Strong?
If you follow all the cold welding procedures, the resulting weld joint will be as strong as the parent metal. However, you must remember that the cold welding technic cannot be applied to brittle (non-ductile) metals, metals with hard surfaces, and metals having carbon content.
In modern cold welding machines for butt joints, cleaning the surfaces will help but may not be mandatory since the oxide layer is removed during diffusion. However, cleaning is a must for lap joints.
Weld Joints
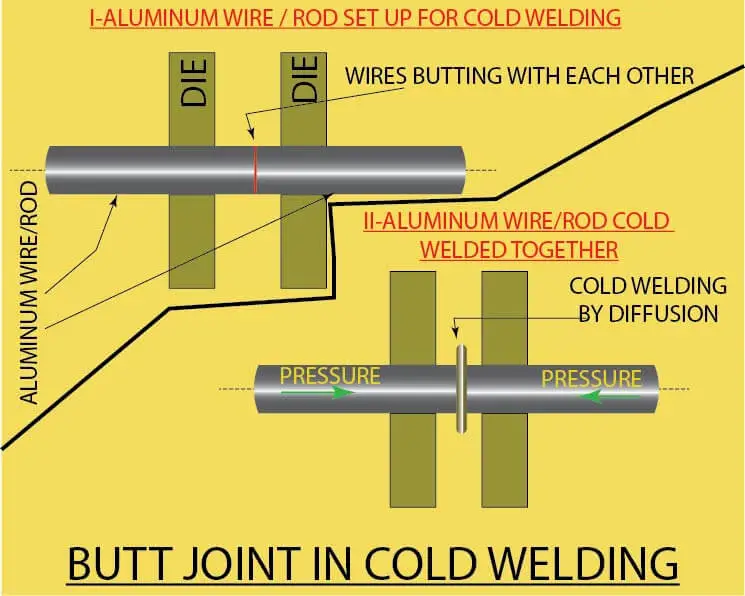
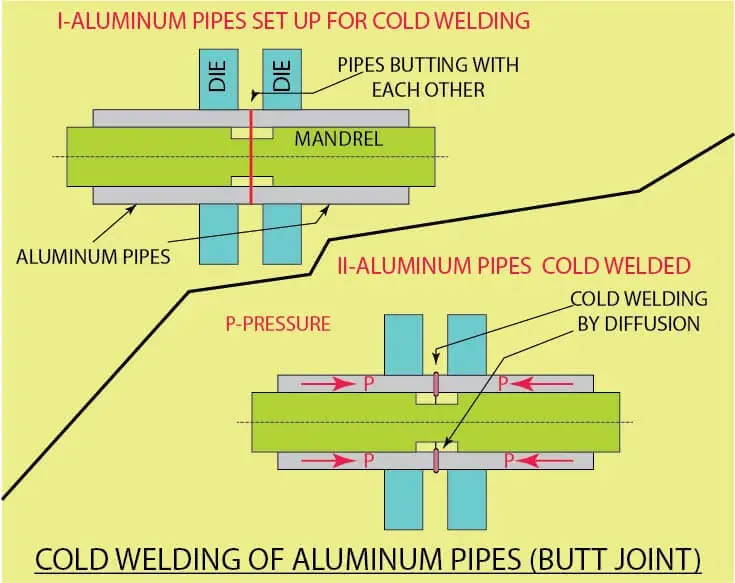
Both butt and lap joints are possible in cold welding. Butt joints are popularly used for welding aluminum and copper wires from 0.5 mm to 10 mm diameter or more. Many cold welding machines have provision to trim the ends of the wire or flat before loading into the machine.
Trimming ensures a clean and flat end. Typically, the pressure is applied to both ends. While doing butt joints, cleaning of the surfaces will help but may not be mandatory since the oxide layer is removed during fusion.
The lap joint can be between the sheets or between the sheet and the rod. While doing the strength calculations, the designer should consider at least 50% thickness of one of the sheets lost because of the pressure applied.
You can make use of the metal drawing process to cold weld multilayer pipes (clad pipes) and clad rods. In the same way, you can pressure cold weld two layers of thin metal by passing them through heavy rollers.
Nano-scale Cold Welding
Cold welding of the macro materials is usually associated with high pressures. On the other hand, scientists have discovered that very thin nanowires of gold having a diameter of 10 microns can be cold-welded within seconds of bringing them in contact by applying minimal pressure.
Intense inspection of nanowires welding indicates an almost perfect joint with properties like strength and conductivity as good as the original metal.
Nano welding is proven between gold and silver, and silver and silver. The high quality of welding achieved in nanowires can be credited to nano-scale dimensions and surface diffusion (with minimal pressure). The latest discovery about Nano-scale welding has good potential in the Nano-fabrication processes.
Cold welding machines
You can do cold pressure welding of most of the non-ferrous ductile metals using the cold welding machine. These machines can handle wires/rods of 0.5 mm and up to 15 mm in diameter.
You can use a hand-operated cold welding machine for smaller diameter wires and pneumatically or electric pneumatically operated machines for higher diameters. These machines usually are portable and can handle both wires and strips.
You have to fit the specific dies on the machine to hold wires and strips, and the dies are adjustable to cover a small range of wire diameters or strip dimensions.
Both parts of the wire or strip to be cold-welded are loaded from the machine’s two sides, and they come into contact with each other under pressure, get diffused, and cold-welded. Many cold welding machines have a guillotine to trim the ends of the metal to be cold-welded.
History of cold welding
You and I may be wondering about cold welding as a new concept; however, it was known to humans centuries ago, and some of the excavated utensils belonging to the Bronze Age are known to have used the concept of cold welding.
Reverend J. I. Desaguliers may be the first to conduct a scientific experiment on cold welding in 1724. He conducted the experiment using two lead balls of the same diameter.
Desaguliers noticed that when the two lead balls are brought into contact, they can stick together by twisting and applying pressure. Further experiments proved that the joint’s strength between the two lead balls was as good as the parent metal.
After that, there were many experiments to explain the science behind cold welding; however, the generally accepted explanation is that cold welding happens due to the formation of a metallic bond between the two metals.
The energy necessary to bind the metal is applied in the form of pressure. Unlike fusion welding, such as arc welding and friction welding, cold welding doesn’t have a molten or a liquid metal phase, which is why it’s referred to as cold welding.
The weld’s mechanical strength can be achieved by following the set procedures like having a perfectly flat and clean surface and exerting proper pressure. The metallic bond is formed between the two metals due to the free movement of electrons between them.
Cold Welding with TIG
There are machines available in the market by the name ‘cold welding machines‘; however, the welding technique adopted in these machines has no relation to the concept of cold welding discussed in the earlier paragraphs.
These machines have a TIG mode and a cold welding mode. When you use it in the TIG mode, you can do TIG welding like any other ordinary TIG welder using filler material, and the welding gun has a tungsten electrode. The machine works using electro spark technology mainly used to repair the defects in aluminum castings and welding very thin sheets or rods.
Unlike regular welding machines, you can touch the welded area of this machine with your bare hand immediately after cold welding, and it is only warm. The weldment quickly absorbs the weld heat. I think this can be the reason for calling this machine a cold welding machine.
Cold Welding in Space
In the previous paragraphs, we have seen how cold welding happens under atmospheric conditions. Let us consider its implications, say, for a spacecraft in space.
When the spacecraft is in space, the two pieces of aluminum used in the spacecraft construction get cleaned over time due to lack of oxygen in space and get cold-welded when it comes in contact. It may happen, even though it was not intended to.
Before going further, let us consider the case histories of Gemini IV and Galileo space crafts.
Gemini IV
Extravehicular activity or EVA is an activity conducted by an astronaut outside his/her spacecraft when it is well beyond the earth’s atmosphere; the term EVA is generally used for a spacewalk.
Ed White was the first American to perform a spacewalk on June 3, 1965, when he was one of the space flight crews of Gemini IV.
Ed White was secured (tethered) to the spacecraft by a kind of hose, and a system was in place to supply oxygen, which also had communications and biomedical instrumentation.
Ed White was on the spacewalk for 21 minutes, and his return to the spacecraft had some anxious moments due to a defect in the hatch door mechanism of the spacecraft, which made closing the hatch door difficult. During that time, the scientists initially suspected the problem was due to cold welding; however, later, it was proved that the problem was due to other reasons.
Galileo
The incident of cold welding in space nearly destroyed NASA’s space operation, costing several billion dollars. On October 9, 1989, NASA had launched a spacecraft called ‘Galileo” into space with the main aim of gathering data about the planet Jupiter.
Considering the considerable distance between the earth and Jupiter, the scientists at NASA had designed a special antenna to complete the mission (the antenna, after it becomes functional, could transmit roughly 80K data per second to the earth station).
The spacecraft Galileo reached Jupiter on April 10, 1991(after 18 months); however, the NASA scientists could not launch the antenna completely. After various studies, the scientists concluded that the antenna’s main mobile structure was stuck together due to cold welding. In the end, the efficiency of the antenna was reduced drastically.
The above incidents forced space scientists to consider the phenomenon of cold welding when designing the spacecraft. To eliminate the threat of unintended cold welding, techniques including coating the parts with a special material may be considered.
Pros of the Cold Welding Process
- The process is a perfect technique for aluminum and copper, including welding aluminum with copper, since it is difficult to weld aluminum and copper by other methods.
- The welding bond created between aluminum and copper by cold welding is sufficiently strong, last longer, and is without any brittle intermetallic compounds.
- Cold welding is extensively used to join or weld wires of different metals, viz. aluminum, copper, silver, nickel, etc. Cold welding gives a perfect weld for the wires and eliminates the problems faced when welding with the use of heat.
- This welding process can be done between dissimilar metals like aluminum and copper and different diameter wires.
- Unlike in the conventional welding process, there is no heat-affected zone.
Cons of Cold Welding
After reading the above paragraphs, you may be wondering why it is not very popular and used in everyday industries.
Cold welding has a positive face, which we have seen; however, there are limitations to using it.
- There are limitations to the types of material that can be cold welded together as the metals must be ductile and can’t have undergone severe hardening processes.
- It is not an easy task to achieve perfect cold welding, and you can achieve a strong cold weld having the same mechanical strength as its parent metals, only if the welding surfaces are flat and you have followed the process techniques correctly. The more flatter and regular the weld surfaces, the easier for perfect cold welding.
- The lack of perfection may be due to various reasons, viz. presence of contamination and oxide layers, irregularities on the surface, etc. The oxide layers and contaminations may be hard to remove, and irregularities on the surface may pose the metals’ problem to bond together (even after a thorough cleaning).
- The cold welding process is possible only for ductile non-ferrous metals like lead, copper, aluminum, etc. The metals should not have undergone any hardening process, including work hardening. This narrows down the metals that can be cold-welded to non-ferrous metals and metals without carbon in it.
The above challenges of cold welding makes it limited to a few areas and cannot be adopted in regular industries where you need to weld different combinations of metals for fabrication parts.
Applications of cold welding
Cold pressure welding is popularly used for joining aluminum and copper wires/rods of diameter 0.5 mm to 12 mm or more, and the weld type is butt joint. A combination of wire metals like aluminum and copper can also be cold-welded.
This process becomes extremely useful when laying underground wire lines where welding with heat is dangerous due to the possibility of the presence of explosive gasses.
The cold pressure welding technique is useful for sealing containers that are sensitive to heat (containers containing explosives for detonating).
Cold pressure welding is used in the electronic industry to manufacture semiconductor devices that are sensitive to heat.
Summary
Let us summarize this article by recalling the topics discussed in a gist:
1. When you bring two non-ferrous ductile metal parts (say aluminum or copper), with clean and flat surfaces into contact under pressure, the two metal parts are joined or cold-welded together due to solid-state diffusion. Cold welding is also known as cold pressure welding or contact welding.
2. Both butt and lap joints are possible in cold welding. Butt joints are popularly used for cold welding aluminum and copper wires from 0.5 mm to 10 mm diameter or more.
3. Scientists have discovered that very thin nanowires of gold having a diameter of 10 microns can be cold-welded within seconds of bringing them in contact by applying minimal pressure, and Nano welding is proved between gold and silver, and silver and silver.
4. Cold pressure welding was known to humans centuries ago, and some of the excavated utensils belonging to the Bronze Age are known to have used the concept of cold welding.
5. Both hand-operated and pneumatically or electric pneumatically operated cold welding machines are available, and most of the machines have portability.
6. Incidents that happened when the spacecraft was in space forced the space scientists to consider the cold welding issues when designing the spacecraft, mainly to eliminate the threat of unintended cold welding.
7. Cold pressure welding has many advantages, including cold welding of aluminum with copper, which was not possible by conventional methods.
8. Cold pressure welding has limitations, such as maintaining a flat and clean surface of the parts to be welded is not easy, and cold welding is limited to non-ferrous ductile metals.
9. Cold pressure welding is widely used to join wires and rods of aluminum and aluminum with copper, sealing containers containing explosives, and the manufacture of semiconductor devices sensitive to heat.
Read: What You Need To Know About LASER Welding.
References: